
Board – CBSE
Std- 9
Topic- Fundamental Unit of Life
Revision Notes
Introduction
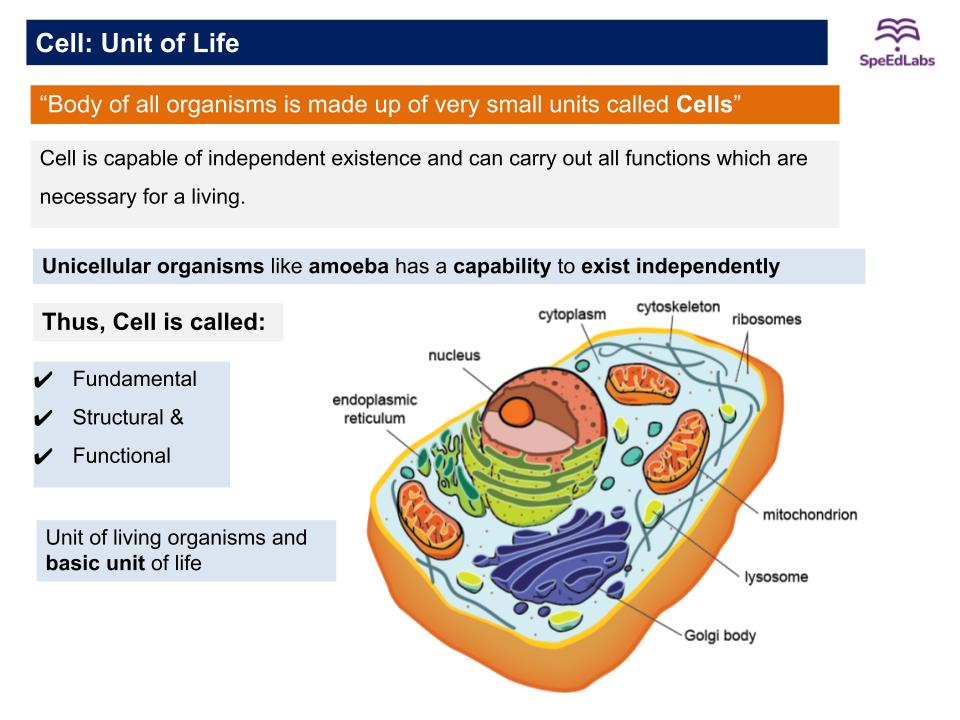
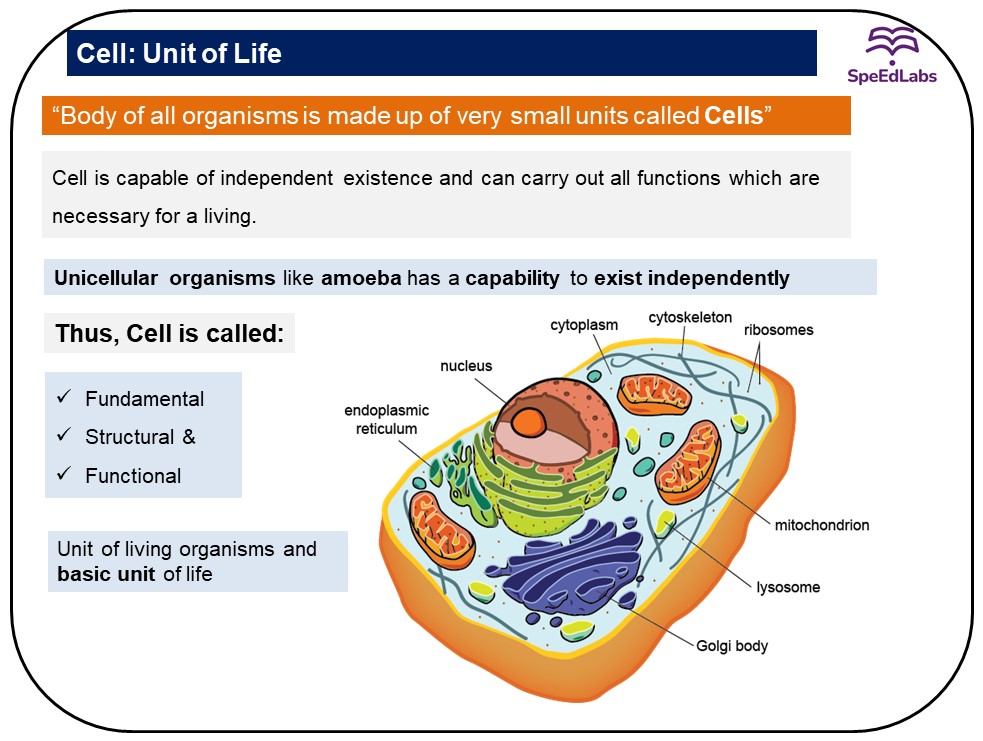
- “Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. It is the basic unit of life”.
- It was discovered by Robert Hook in 1831 in a cork slice.
- Leeuwenhoek (1674) discovered the free-living cells in pond water.
The cell theory
- Cell is the basic unit of life and was presented by two biologists, Schleiden and Schwann.
- The cell theory by Virchow suggests that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Types of organisms
- Unicellular Organism: These organisms are single-celled which perform all the functions. Examples: Amoeba, paramecium, bacteria.
- Multicellular Organism: Many cells are grouped together to perform a different function in the body and also form various body parts. Examples: fungi, plants, animals.
Types of cells
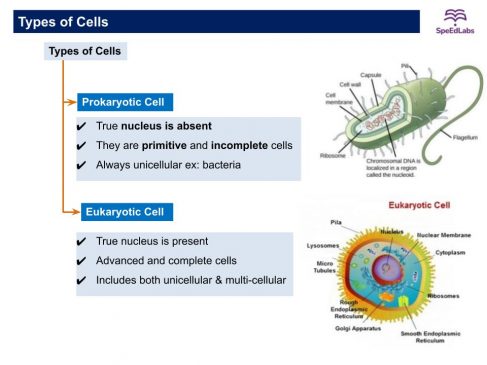
There are two types of cells:
(i) Prokaryotes
(ii) Eukaryotes
|
Prokaryotes |
Eukaryotes |
| Cells of organisms lack nuclear membrane. | Cells of an organism have a nuclear membrane. |
| The nucleolus is absent. | The nucleolus is present. |
| Single chromosomes. | Single or multi chromosomes |
| Reproduction is always asexual. | Reproduction is both sexual and asexual. |
| Always unicellular. | Often multicellular. |
| Membrane-bound cell organelles are
absent. |
Membrane-bound organelles are present like
mitochondria. |
| The centriole is absent. | The centriole is present only in animal cells. |
| Cell division is by binary fission. | Cell division is by mitosis or meiosis. |
| Example: Bacteria, Blue-green algae,
etc. |
Examples: Fungi, Plant cells, Animal cells, etc. |
Difference between Animal Cell and Plant Cell
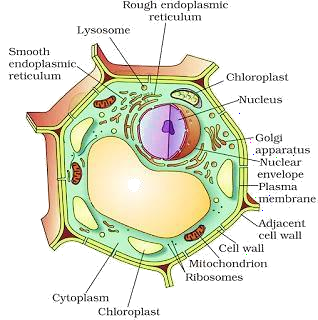
|
Animal Cell |
Plant Cell |
| The cell wall is absent. | The cell wall is present. |
| Plastids are absent. | Plastids are present. |
| Centrioles are present. | Centrioles are absent. |
| Golgi bodies are present. | Golgi bodies are present and called dictyosomes. |
| Vacuoles are absent. If present, they are small. | Vacuoles are present and large in size. |
| A centrosome is present with one or two
centrioles. |
Centrosome is absent |
Diffusion
- The random movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to the region of low concentration is called diffusion.
- Some substances like carbon dioxide or oxygen can move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion. The cell also obtains nutrition from the environment.
Osmosis
- The movement of water molecules through the selectively permeable membrane along the concentration gradient is called osmosis.
- Plant cells tend to obtain water through osmosis.
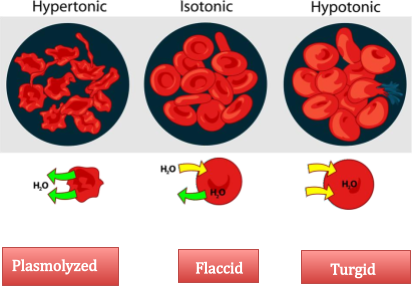
Behave of cell in Hypotonic or Hypertonic or Isotonic solution
| Name of the solution | Condition | Result |
| Hypotonic solution | The medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell. | The cell will gain water by osmosis and is likely to swell up. |
| Isotonic solution | Medium has exactly the same water concentration as the cell. | Water crosses the cell membrane in both directions.
The cell will stay the same size. |
| Hypertonic solution | Medium has a lower concentration of water than the cell. | Water crosses the cell in both
directions, but more water leaves the cell than enters it. |
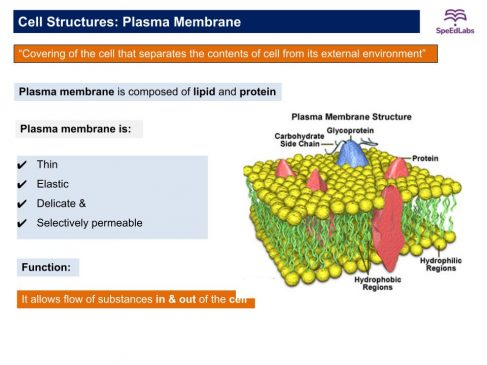
Plasma membrane or Cell membrane
- The outermost covering of the cell separates the contents of the cell from the external environment.
- It regulates the entry and exit of substances through the cell (selectively permeable membrane).
- It is made up of lipid and protein.
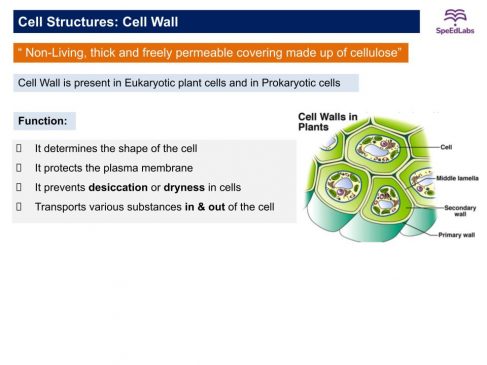
Cell Wall
- Cell wall is another rigid outer covering in addition to the plasma membrane found in a plant cell.
- The plant cell wall is mainly composed of cellulose.
The function of the Cell wall
- Cell wall permits plants, fungi, and bacterial cells to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting.
- Prevent cells from extreme conditions.
Plasmolysis
- When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis, it causes shrinkage or contraction of the cell away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is known as plasmolysis.
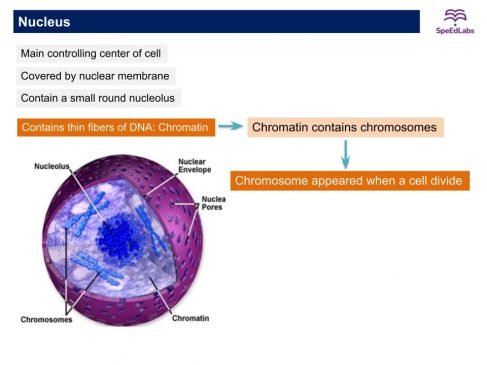
Nucleus
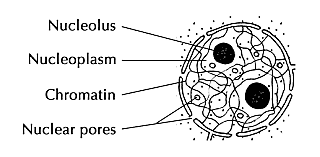
Composition of Nucleus
- The nucleus has a double-layered covering called a nuclear membrane.
- The nuclear membrane has pores that allow the transfer of material.
- The nucleus contains chromatin fiber, (Chromosomes are visible in a dividing cell).
- Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein.
Functions of chromosomes
- Chromosomes contain hereditary information.
- DNA molecules contain the information necessary for cellular activity.
- Functional segments of DNA are called genes.
Functions of Nucleus
- The nucleus plays a central role in cellular reproduction.
- It directs the chemical activities of the cell.
Nucleoid
- In some organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane.
- Such an undefined nuclear region containing only nucleic acids is called a nucleoid.
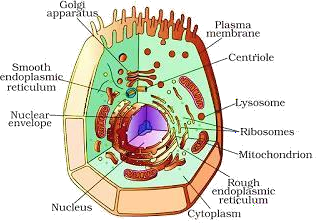
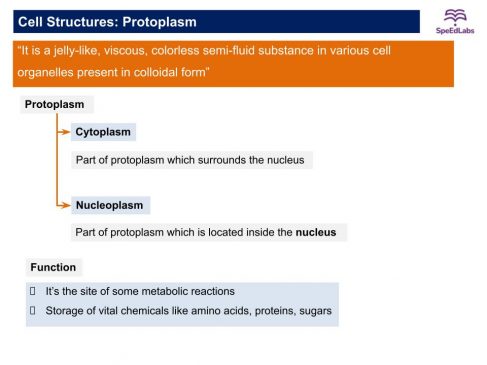
Cytoplasm
- The cytoplasm is the fluid inside the plasma membrane.
- It also contains many specialized cell organelles.
Function of Cytoplasm
- It helps in the exchange of material between cell organelles.
- It stores vital chemicals such as amino acid, glucose, vitamins, and iron, etc.
- It is the site of certain metabolic pathways such as glycolysis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large network of membrane bound sheets.
- It looks like long tubules or round or oblong bags (vesicles).
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
(i) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
(ii) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)

Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum
- RER has ribosomes attached to its surface. Ribosomes are the main site of protein synthesis.
- The SER helps in the synthesis of lipids.
- Some of these proteins and lipids help in building the cell membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis.
- Some other proteins and lipids function as enzymes and hormones.
- One function of the ER is to serve as a channel for the transport of materials.
- In the liver cells, SER plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs.
Golgi Apparatus
- The Golgi apparatus consists of membrane-bound vesicles arranged parallel to each other in stacks called cisterns.
- These membranes often have connections with the membranes of ER.
The function of Golgi Body
- The material synthesized near the ER is packaged and dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell through the Golgi apparatus.
- Its functions include the storage, modification, and packaging of products in vesicles. The Golgi apparatus is also involved in the formation of lysosomes.
Lysosomes
- They keep the cell clean by digesting any foreign material.
- Lysosomes have a membrane-bounded structure filled with digestive enzymes.
Functions of Lysosomes
- Lysosomes break foreign materials entering the cell.
- When a cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst and the enzymes digest their own cells.
- Therefore, lysosomes are also known as the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell.
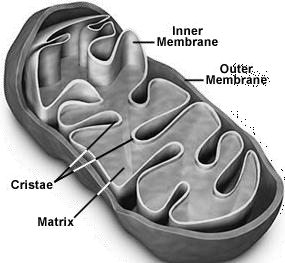
Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell
Structure of mitochondria
- Double membrane structure,
- The outer membrane is very porous.
- The inner membrane is deeply folded to increase surface area
Functions of mitochondria
- Released energy by respiration in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) molecules.
- Mitochondria have their own DNA and ribosomes. Therefore, mitochondria can make some of their own proteins.
Plastids
- Plastids are present only in plant cells.
- There are three types of plastids:
- Chromoplasts (colored plastids).
- Leucoplasts (white or colorless plastids).
- Chloroplasts (contains chlorophyll).
Structure of Plastids
- The internal structure consists of numerous membrane layers embedded in the stroma.
- Plastids also have their own DNA and ribosomes like mitochondria and are similar to their structure.
Function of Plastids
- Chloroplasts are important for photosynthesis in plants.
- Leucoplasts are primarily organelles in which materials such as starch, oils, and protein granules are stored.
Vacuoles
- Vacuoles are storage sacs for solid or liquid contents.
- They are small-sized in animal cells while plant cells have very large vacuoles.
Function of vacuoles
- In plant cells vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity and rigidity to the cell
- Many important substances are stored in vacuoles like amino acids, sugars, and proteins.
- In single-celled organisms like Amoeba, the food vacuole contains the food items that the Amoeba has consumed.
Video Summaries
1)Introduction
2)Basic Structure of Cell
3)Types of Cell
4)Cell Structure: Cell wall and Cell Membrane
5) Cell Organelles: Part-1
6)Cell Organelles: Part-2

